There was a time when the Fuerza Aérea Argentina (Argentine Air Force) was considered to be one of the best Air Forces in Latin America, if not the world. Created into its own independent entity out of the Argentine Army in 1945, the Argentine Air Force began a massive modernization program which saw them becoming the first country in South America to operate jet aircraft.
This occurred when they took delivery of British made Gloster Meteors in 1947. As well as operating a formidable bomber force that was made up of Avro Lincolns and Lancasters, all of which were also acquired from Britain.
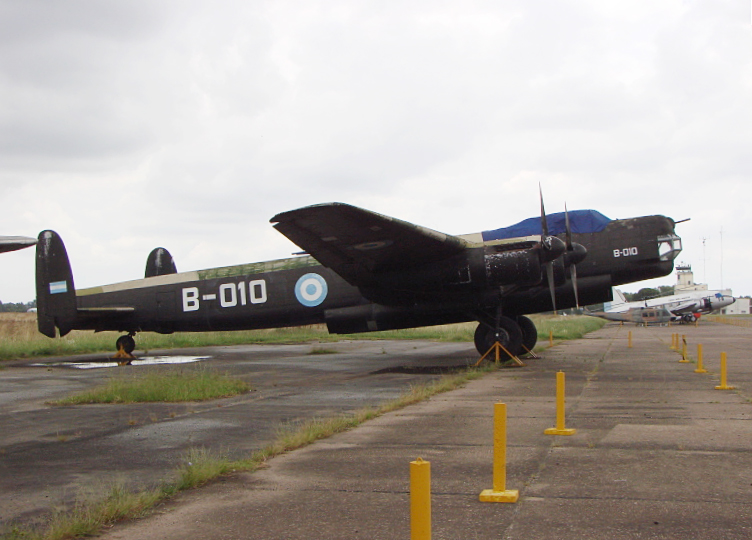

In later years, Argentina went as far as attempting to develop their own indigenous jet aircraft with the aid of former Luftwaffe personnel and other German engineers. A program which resulted in the creation of the FMA IAe 33Pulqui II, making Argentina the first country in Latin America to develop its own jet aircraft and 6th in the world to do so. Even though the Pulqui never entered service (the Government had decided to purchase F-86 Sabers from the U.S. Instead.) , it still showed just what the Argentine Air Force was truly capable of and as the years passed, they continued to build up its fleet by adding newer and more advanced aircraft to its already impressive line up.

But that all changed in the 1980’s, the Falklands War in 1982. Where in an attempt to shift attention away from their troubled economy, the Military Junta which ruled the Latin American country at the time, invaded the British Territories of East and West Falklands.
Thinking that the British government (who had supplied Argentina with a number of military equipment in the years before the invasion) would be unable, if not unwilling, to commit military forces to retake the islands.
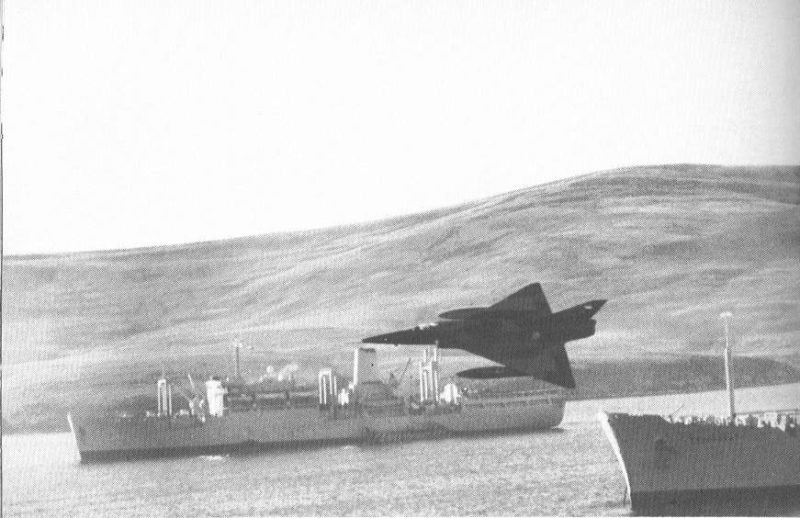
The resulting conflict saw the Argentine Air Force sustain heavy losses, losing dozens of fighters, helicopters, cargo aircraft, and even two Canberra Bombers, the majority of which were shot down by Royal Navy and Royal Air Force Harrier jets.
Many had believed to be no match for Argentina’s fleet of supersonic Mirage jet fighters.
By contrast, the Argentine Air Force could only boast of one air to air kill when 2 IA-58 counter-insurgency aircraft shot down a scout helicopter during the battle of Goose Green. Even though both the air force and navy had gained some successes during the conflict, it still was not enough to secure a victory for Argentina as the British were able to retake the islands just after two months since the war began. It also did not help that a number of aircraft and equipment had been captured and shipped back to Britain after the Argentine surrender.

The years following the war saw the Argentine military as a whole and especially the Argentine Air Force , took a sharp decline as the country’s economy worsened and traditional arms suppliers placed arms embargos on their former client.
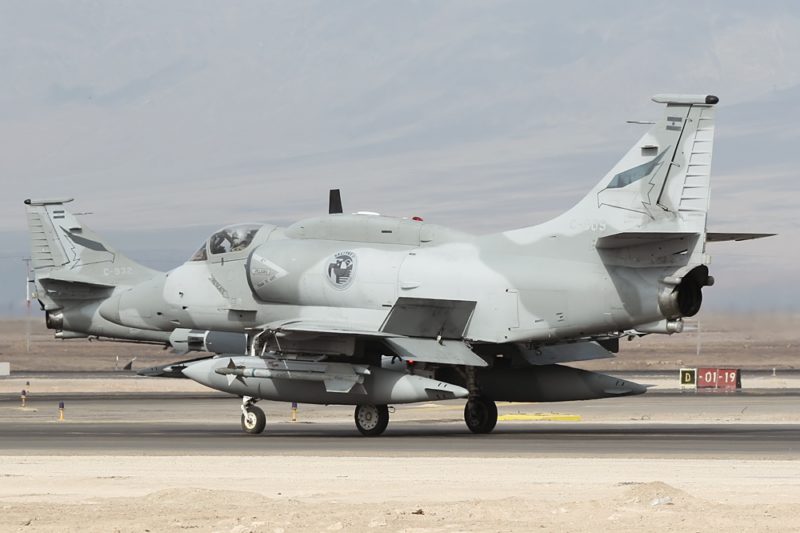
This saw the Latin American nation unable to procure new assets. After some of these embargoes were lifted in the 1990s and Argentina was able to acquire upgraded A-4s from the United States, the military still continued their steady decline throughout the decade and into the 2000s.
Today, the Argentine Air Force is nothing more than a shadow of its former self. 2015 saw the Argentine Air Force retiring their remaining Mirage and Dagger Fighters, as their airframes had reached a point where they were no longer safe to fly.
Leaving only their remaining fleet of A-4AR “Fighthawks” and IA-63 advanced jet trainers to fill the gap left by these aircraft. Both of which are unsuited for air to air combat and are largely outmatched by aircraft used by their neighbors Chile and Brazil. Even more so, a shortage of spare parts could also see their A-4 fleet being grounded in the near future.

Recent attempts to acquire new aircraft such as the Chinese JF-17, the Swedish Saab Gripen (which is made with British components) and even secondhand Kifr jets from Israel have all failed due to either technological, political, or economic restrictions suffered by the Argentine government.
Problems in the air force also extend to their fleet of C-130 transport aircraft, as their airframes are starting to show their age. These aircraft provide a vital component of the air force, as they are used to not only supply Argentina’s arctic bases, but also assist in supplying their peace keeping contingents in Haiti and Cyprus. Though these aircraft have undergone major upgrades, and Argentina has shown interest in acquiring new aircraft to replace the C-130s, it is unknown whether if they would be able to keep their current fleet flying for long, or even if they will have a transport wing as the economic situation in the country worsens.
It is believed that in the years to come, the Argentine Air Force will cease to exist as a major military component of the Argentine Armed Forces and with an economy in shambles and embargoes still in place due to the Falklands war, it is still unknown whether if the Argentine Air Force will ever fully recover. It is possible that what was once Latin America’s most formidable air forces, maybe flying into the sunset for the last time.










You have right in everything , my fhather was a former pilot who flew mirage and A4 in the argentine air force, but the situation it’s worst. The only thing to add to your article it is the quantity of ships that wingsmen of my fhathers sunk and hit during the malvinas conflic.
Patrick Morrison, tu lectura de la guerra de Malvinas es tendensiosa y desinformada. Explicame que paso con las fragatas Sheffiel, el Camberra, el ataque y fuera de servicio del portaviones Invensible, La Sir Galland, El Conqueror y demás aviones harrier y helicopteros que fueron hundidos y derribados. Si, es cierto que ustedes tenían mayor poderío y ayuda de la NATO, pero no podes decir que Argentina no peleo y que para ustedes fue un paseo pelear en el Sur Argentino, cuando muchos de los ex-combatientes británicos han quedado con secuelas por la dureza de las batallas. Soy argentino, tengo la edad de los ex-combatientes de nuestras Malvinas, y a Inglaterra no le sobraba nada para seguir luchando. Nuestros problemas internos llevaron a una falta de coordinación de las fuerzas, pero nuestros soldados y pilotos pelearon con coraje y dedicación, no tomes esta guerra con la liviandad de tus palabras, porque ofendes la memoria de los muertos y la inteligencia de los vivos. La mejor forma de conocer los hechos es leer e instruirse sobre los temas a difundir.
Sr. Patrick Morris: Su desconocimiento de la historia de mi país es lamentable. Ud, antes de escribir algo, debería estudiar, al menos los antecedentes relacionados con el tema a tratar. Como inicio debería saber que Argentina, no invadió “territorios británicos”, sino que recuperó las tierras que en 1883 Inglaterra usurpó, invadiendo los territorios de las islas Malvinas y desalojando por la fuerza a las autoridades argentinas instaladas en las islas, desde mucho tiempo antes, sin querer hablar aquí de los antecedentes históricos, geográficos y políticos que nos asignan los derechos soberanos sobre esos territorios. Pero no importa, pasará otro siglo o varios más, pero las tierras y espacios marítimos que las circundan, regresarán a la soberanía nacional, por más que a Ud. le pese.
La hegemonía imperial de Gran Bretaña, hace muchos años que quedó atrás, los tiempos han cambiado y la historia se reescribirá. Ya lo verá Ud..
Atentamente.
Br (R) VGM Otto Adolfo Ritondale
tritoncuarenta@gmail.com
Hi there everyone, it’s my first pay a visit at this web page,
and article is actually fruitful for me, keep up posting these content.
Patrick, as of now 2019, the Argentine military is in a worse state. The Argentines just don’t have the military history or tradition that the British have, and the quality of the British armed forces is far superior, please Argentina stick to football and dancing.